August 23, 2023
Introduction
Social and emotional learning (SEL) is a set of skills and processes that enable learners to develop healthy identities, manage emotions and achieve personal and collective goals, feel and show empathy for others, establish and maintain supportive relationships, and make responsible and caring decisions. (CASEL, 2023) SEL is a “learner-centered” development strategy, focusing on the personal growth and development of the child or learner rather than the accumulation of discipline—or career-advancing information. (Schiro, 2013) As progressive education viewpoints, such as learner-centered ideology, have become more popular and mainstream in United States schooling, SEL programs are being more widely implemented throughout United States schools, with more than 90 percent of schools and districts reporting a focus on SEL development as of 2020, backed by a wide base of research. (Gagnier, Okawa, & Jones-Manson, 2022)
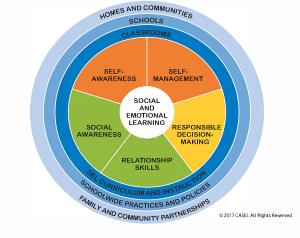
One organization, the Collaborative for Academic, Social, and Emotional Learning (CASEL), divides essential SEL competencies into five categories: self-awareness, self-management, responsible decision-making, relationship skills, and social awareness. CASEL analyzes many in-school SEL programs to determine their effectiveness…